Starting a bottling water production business, whether it is jug water or small bottles, has the advantage that you can start with a small water purification plant, with a smaller investment, and then if demand grows, add or grow your equipment. You can also plan alternative sources of financing in case you do not have adequate capital.
First step before making the decision to install a water purifier.
Make a business plan.
A detailed business plan is the most important tool you need to start your project. It would give you a clear idea of what you want to accomplish and how much capital and skills you need to achieve it. A business plan for a bottled water purification plant could start with equipment alone costing $40,000 but it is not only the equipment that needs to be considered, let’s list what we need to take into account to afford the project.
- Market study to see how many water purification plants there are in the area and the cost per carafe or bottle.
- Cost of renting or purchasing a commercial space.
- Cost and requirements for trademark registration, COFEPRIS permits and Civil Protection review.
- Employee salaries, benefits and tax payments.
- Cost of water per m3 of raw water and cost already treated.
- Cost of consumables: bottles and caps, chemicals, analysis equipment, labels, filter media, softener salt, cartridges and membranes (and their frequency of change) and cleaning products in general.
- Delivery vehicle, spare parts, wear and tear and maintenance.
- Investment in internet advertising, social networks, flyers or web page.
- Your cost per hours worked, at the beginning most likely won’t be there for your salary, but you have to have the cost of your time invested.
Source of supply for the purification plant.
Is a good source of water supply necessary? This is an important point when choosing a location for the purifier. If the water is from the municipal network or from a well, it is necessary to make a physical-chemical analysis of the water, since water of poor quality or with more contaminants to be eliminated by the purifier will require larger equipment and a higher maintenance cost. The recommendation is to locate your production plant in a place with better water quality and look for a way to transport the water to a water bottling plant to be bottled. There are companies that sell water from springs or sources of better points in pipes.
Again, you will have to evaluate the costs of the water, if it requires more frequent relocation or maintenance, change of activated carbon, softener resin or membrane clogging, in case you have low quality water, this depends on your location and your specific needs.
What equipment does a water purifier need?
In Mexico, the permissible limits of contaminants in water for human use and consumption are dictated by standards:
- NOM-127-SSA1-2021, “Water for human use and consumption. Permissible limits of water quality”.
- NOM-201-SSA1-2015, “Products and services. Water and ice for human consumption, packaged and in bulk. Sanitary specifications.”
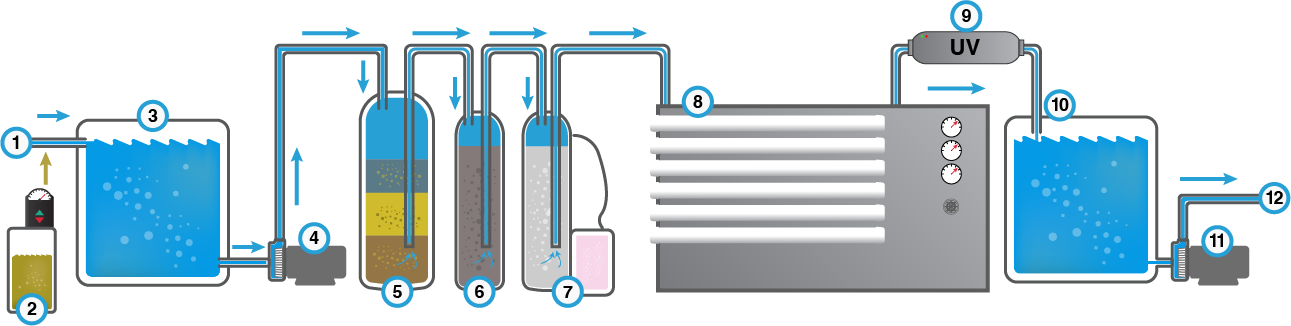
First stage of a water purification plant: Raw water feeding.
Identify the quality of the incoming water to our water purification plant, either from the municipal drinking water network, from wells, from surface water from lakes or rivers, or from the purchase of water pipes from the same supplier, and do not make variations of water sources that we have not well studied.
Second stage of purification: Water disinfection.
The cheapest and most common disinfectant is chlorine, although other options such as chlorine dioxide are also available. These chemical agents help eliminate dangerous and undesirable microorganisms from the water. For this to be effective, it is necessary to give the chlorine enough contact time to do its job.
Chlorine dioxide can be a good water disinfectant, plus it can be produced on site and not to have too much in storage.
Third stage: Raw water storage tank.
Commonly this tank apart from storing enough water for the peak flow of water demand. It is also used to give the water adequate contact time with chlorine.
Fourth stage of a water purifier: Water purifier feed pump.
It must be properly selected for the maximum flow rate of the equipment (commonly backwash) and withstand the pressure drop generated by the equipment and piping sufficient to feed the reverse osmosis system (commonly between 30 and 60 psi pressure), all while operating at its highest possible efficiency range.
Another option is to place a hydropneumatic tank separate from the pump to maintain a constant pressure in the line at all times.
Fifth stage of a water purification plant: multimedia filter or deep sediment bed.
Granular media are regularly used, although in recent years disc filters are becoming a more economical and competitive investment for water flows greater than 9 m3/h. In some regions, depending on the water source, a catalytic granular media may be required to remove iron, manganese and hydrogen sulfide. This can be used instead of the granular or disc media filter, or just after the sediment filters, depending on the quality of the raw water to be treated.
Sixth stage of a water purifier: granular activated carbon bed filter.
Granular activated carbon works excellently in adsorbing organic compounds which are guilty of producing a bad odor, color and taste to water, and can even be toxic. In addition to adsorbing organic compounds, it acts as a reducing agent for free chlorine and converts it to chloride ion (Cl-). It is important to disinfect the activated carbon beds because, being an adsorbent of organic matter, it is a favorable medium for bacterial growth.
Seventh stage of a water purifier: hard water softener.
This step is recommended when the water is to be osmotized because high CaCO3 concentrations can foul the reverse osmosis membranes, compromising the proper functioning of the system and the membranes. The concentration of CaCO3that can be fed to a membrane varies among manufacturers. It is also necessary to soften when our concentration is higher than the permissible limit by the standard which is 500 mg/L as CaCO3.
Eighth stage of a water purification plant: reverse osmosis system.
This system is necessary when it is required to reduce the concentration of dissolved salts in it (STD), the amount of salts that are removed during this process depends on the membrane since there are different types of membranes, usually ranging from 99%. Something very important to take into account is that reverse osmosis systems generally generate a 50% rejection of water concentrated in salts. This means that we will produce half of the water without dissolved salts that we feed to our RO system. Depending on the water quality required, multi-membrane or series-pass designs are designed.
Ninth stage of a water purifier: UV light lamp.
Last stage of disinfection prior to point of use, only as a protective barrier to eliminate microorganisms. The water is passed through a chamber with a UV light source at a suitable wavelength to prevent bacterial growth. The lifetime of the UV light source depends on the brand.
Tenth stage of a water purification plant: product water storage tank.
This tank allows us to store the water before bottling or the high demand needed in the process, in some occasions that the water is going to be stored for more than 3 days, it is necessary to use an Ozone generator, to keep the water without bacteriological contamination or microorganisms without adding a chemical that leaves a residue in the water.
Eleventh stage of a water purification plant: product water pump.
The pressurizing pump at this point helps us to fill and wash bottles or demijohns faster, also to transfer water to a production line or to put pressurized water in a hotel or offices.
Last stage of a water purification plant: point of use or filling of jugs or bottles.
We arrive at the point of use of purified water, which can be used in the filling of demijohns, washing of demijohns, small PET bottles, industrial use in a production line, use of industrial kitchens and canteens or services for hospitals or hotels, pre-treated water for laboratories that may require other processes to make demineralized water.
Conclusion
The challenge at the beginning may be to raise capital to launch a business idea. Your idea must be viable and well studied so that you can get financing from financial institutions or investors from relatives or acquaintances. The first thing to do before seeking capital for the project is to write a detailed business plan. With a good business plan, you can easily convince investors to invest in your business. The truth is that no bank can grant you a loan if you do not have a good and viable business plan.
Once the water purification plant has started, we recommend taking great care of consumables, lids, quality of the demijohns, keeping a close eye on the cost of the finished product in order to maintain the profit margin, taking care of the maintenance and analysis logs for possible sanitary revisions.
More related articles:
- What is deep bed filtration?
- What is a water softener?
- How does ultraviolet UV light work for water disinfection?
- Chlorine dioxide as water disinfectant
Source: https://www.profitableventure.com/bottled-water-company-cost/